Статический IP-адрес с NetworkManager?
Я просто хотел настроить статический IP-адрес для машины fedora 19 в моей локальной сети. Я привык к /etc/network/interfaces из Debian, но этот файл не существует здесь.
Немного погуглив, я нашел небольшой учебник, в котором сказано отключить NetworkManager через systemctl и включить сеть. После этого можно настроить статический IP-адрес в файле с именем /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-*interfacename*,
Вот моя первая проблема: я нашел файл с MAC-адресом моего интерфейса, который отображается ifconfig но имя после ifcfg- не совпадает с именем из ifconfig. Почему это так?
Моя вторая проблема связана с использованием NetworkManager.service или network.service. Я прочитал на форуме, что network.service по-прежнему включен по соображениям совместимости и может быть вскоре исключен. Если network.service скоро будет заменен NetworkManager.service, я не должен выбрать NetworkManager.service для настройки моих сетевых интерфейсов? Если да, то как мне это сделать с NetworkManager из оболочки?
Редактировать:
Вот требуемые результаты:
[root@bitch /]# ifconfig
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host>
loop txqueuelen 0 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 97 bytes 12042 (11.7 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 97 bytes 12042 (11.7 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
p3p1: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.178.11 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.178.255
inet6 fe80::214:85ff:febc:1c63 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 00:14:85:bc:1c:63 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 134347 bytes 169988336 (162.1 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 78199 bytes 6595669 (6.2 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 1 carrier 0 collisions 0
[root@bitch /]# ls -l /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/
total 200
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 437 Sep 15 02:05 ifcfg-enp2s5
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 254 May 31 09:49 ifcfg-lo
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 24 Jun 27 19:12 ifdown -> ../../../usr/sbin/ifdown
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 627 May 31 09:49 ifdown-bnep
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 5553 May 31 09:49 ifdown-eth
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 781 May 31 09:49 ifdown-ippp
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 4141 May 31 09:49 ifdown-ipv6
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 11 Jun 27 19:12 ifdown-isdn -> ifdown-ippp
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 1642 May 31 09:49 ifdown-post
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 1068 May 31 09:49 ifdown-ppp
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 837 May 31 09:49 ifdown-routes
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 1444 May 31 09:49 ifdown-sit
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 1462 May 31 09:49 ifdown-tunnel
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 22 Jun 27 19:12 ifup -> ../../../usr/sbin/ifup
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 12445 May 31 09:49 ifup-aliases
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 859 May 31 09:49 ifup-bnep
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 10234 May 31 09:49 ifup-eth
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 12033 May 31 09:49 ifup-ippp
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 10437 May 31 09:49 ifup-ipv6
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 804 May 31 09:49 ifup-ipx
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 9 Jun 27 19:12 ifup-isdn -> ifup-ippp
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 642 May 31 09:49 ifup-plip
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 1043 May 31 09:49 ifup-plusb
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 2609 May 31 09:49 ifup-post
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 4154 May 31 09:49 ifup-ppp
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 1925 May 31 09:49 ifup-routes
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 3268 May 31 09:49 ifup-sit
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 2607 May 31 09:49 ifup-tunnel
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 3775 May 31 09:49 ifup-wireless
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 4623 May 31 09:49 init.ipv6-global
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 13836 May 31 09:49 network-functions
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 26134 May 31 09:49 network-functions-ipv6
Содержимое / etc / sysconfig / network-scripts / ifcfg-enp2s5:
PEERROUTES="yes"
IPV6INIT="yes"
NAME="enp2s5"
IPV6_PEERDNS="yes"
DEFROUTE="yes"
UUID="7622e20e-3f2a-4b5c-83d8-f4f6e22ed7ec"
PEERDNS="yes"
IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL="no"
HWADDR="00:14:85:BC:1C:63"
BOOTPROTO="static"
IPV6_DEFROUTE="yes"
IPV6_AUTOCONF="yes"
IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL="no"
TYPE="Ethernet"
ONBOOT="yes"
IPV6_PEERROUTES="yes"
IPADDR=192.168.178.11
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
BROADCAST=192.168.178.255
NETWORK=192.168.178.0
GATEWAY=192.168.178.1
Grepping dmesg для udevd:
[root@bitch network-scripts]# dmesg | grep udevd
[ 0.788381] systemd-udevd[97]: starting version 204
[ 2.457296] systemd-udevd[322]: starting version 204
[ 3.110272] systemd-udevd[329]: renamed network interface eth0 to p3p1
2 ответа
Command-Line Instructions
After much digging, I found that the ifcfg-* file names, and the NAME= variable in the file have very little to do with the actual assignment. You can literally change them to whatever you want... I did a test on my machine changing them to eth0 and the manual/static IP was still applied upon startup. The key here seems to the be HWADDR variable inside the file. NAME= value only seems to be the name displayed in the graphical Network Manager settings. So, that being said I believe all you need to do is...
Удостовериться
NetworkManager.serviceis still enabled, andnetwork.serviceвыключен.The most IMPORTANT step is to delete the current ifcfg-enp2s5 script.
sudo rm /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp2s5Create a new script named ifcfg-p3p1
sudo nano /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-p3p1Set the contents of ifcfg-p3p1 to the following, and update the respective IP settings with your desired settings.
TYPE=Ethernet BOOTPROTO=none DEFROUTE=yes IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6INIT=yes IPV6_AUTOCONF=yes IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no NAME=p3p1 UUID=7622e20e-3f2a-4b5c-83d8-f4f6e22ed7ec ONBOOT=yes DNS1=10.0.0.1 IPADDR0=10.0.0.2 PREFIX0=24 GATEWAY0=10.0.0.1 HWADDR=00:14:85:BC:1C:63 IPV6_PEERDNS=yes IPV6_PEERROUTES=yes
As for why the ifcfg-* name was different from the actual device name. I don't know but suspect it has something to do with how the Network settings were applied during installation.
Graphical Instructions
- Open System Settings
- Click on Network
- Click on Options...
- Click on the IPv4 Settings* or IPv6 Settings tab depending on what IP version your home network is using (most likely IPv4 ).
- Click on the Method combo-box and select the Manual option.
- Click on the Add button.
- Type the address you want in the Address columns (eg 10.0.0.20).
- Type the netmask for your network in the Netmask column (eg 255.255.255.0).
- Enter the gateway (usually your router's IP) in the Gateway column (eg 10.0.0.1)
Enter your DNS server in the DNS servers text-box (eg 10.0.0.1)
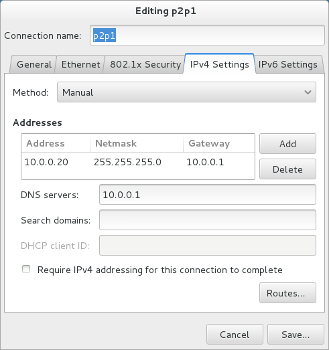
- Click on Save...
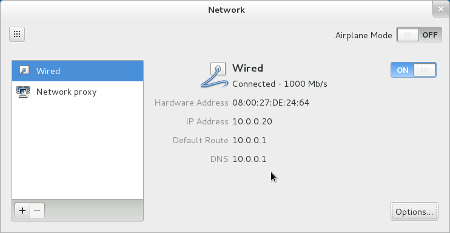
- When you return to the Network settings, turn the Wired interface OFF .
It should automatically turn back on with the static address information you entered in the previous steps. If it does not turn on, click the toggle switch to turn it on.
To answer your question about using the NetworkManager.service над network.service , There is definitely potential it could be removed in later releases. As a general rule of thumb though, no matter the topic is, you should always try to avoid using anything "included for backwards compatibility" . So, you should stick to using NetworkManager if you can .
Я не использую Fedora, но, согласно этому сообщению, файл, который вы ищете, должен быть /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-p3p1 который должен выглядеть примерно так:
DEVICE=eth0
BOOTPROTO=none
HWADDR=00:13:20:5E:C0:47
ONBOOT=yes
DHCP_HOSTNAME=balthasar.benhome.com
TYPE=Ethernet
USERCTL=no
IPV6INIT=no
PEERDNS=no
IPADDR=172.16.3.3
NETMASK=255.255.255.192
GATEWAY=172.16.3.1
Настройка IP там должна работать.